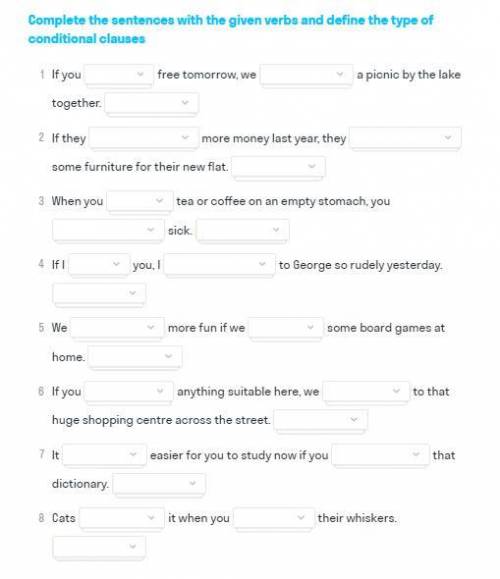
Complete the sentences with the given verbs and define the type of conditional clauses
Другие вопросы по теме Английский язык
Популярные вопросы
- Решения с расстановкой коэффициентов прикрепить...
3 - Дано вектори: a(-5;1), p(x,y), n(-2;7), a+p=n. Знайти: x,y...
2 - Які чинники зумовили набір машинобудівних виробництв, що є галузями...
3 - ЗАДАНИЕ 2. Вставьте вместо точек нужные по смыслу слова. Объясните...
3 - В параллелограмме острый угол равен 30°, а его стороны равны 16 см...
2 - Ребята, это очень два упражнения ...
2 - Як називається південний край африкиі хто його відкрив? будь ласка...
2 - Який рух вважають періодичним...
3 - 3. Найдите значение выражения: (a2 – b)/a –а , при а = 0,2, b = –...
2 - АВ=3, АС=2, угол А=60. Найти ВС....
2
This is a type 1 conditional sentence. It describes a possible future condition and its possible result.
Explanation: The sentence is structured in the following way: If (condition), (result). The condition is "If I study hard," and the result is "I will pass the exam." The verb "study" is in the present tense, indicating a future action if the condition is fulfilled. The verb "will pass" is in the future tense, showing the result of the condition being met.
2. If it rains, I will stay at home.
This is also a type 1 conditional sentence.
Explanation: The sentence follows the same structure as the previous one. The condition is "If it rains," and the result is "I will stay at home." The verb "rains" is in the present tense, indicating a possible future event, and the verb "will stay" is in the future tense, showing the result of the condition being met.
3. If I had studied, I would have passed the exam.
This is a type 3 conditional sentence. It describes a past unreal condition and its unreal past result.
Explanation: The sentence is structured as follows: If (past unreal condition), (unreal past result). The condition is "If I had studied," indicating that the studying did not actually happen in the past. The result is "I would have passed the exam," indicating that the passing of the exam did not actually occur in the past. The verbs "had studied" and "would have passed" are in the past perfect tense, indicating an unreal past condition and result.
4. If I go to bed late, I will be tired in the morning.
This is a type 1 conditional sentence.
Explanation: The sentence follows the same structure as the previous examples. The condition is "If I go to bed late," and the result is "I will be tired in the morning." The verb "go" is in the present tense, indicating a possible future action, and the verb "will be" is in the future tense, showing the result of the condition being met.
5. If she doesn't hurry, she will miss the bus.
This is also a type 1 conditional sentence.
Explanation: The sentence follows the same structure as the previous examples. The condition is "If she doesn't hurry," and the result is "she will miss the bus." The verb "doesn't hurry" is in the present tense, indicating a possible future action, and the verb "will miss" is in the future tense, showing the result of the condition being met.
Overall, these sentences demonstrate different types of conditional clauses. Type 1 conditional sentences describe possible future conditions and results. Type 3 conditional sentences describe unreal past conditions and unreal past results. It is important to understand the different types of conditional clauses to accurately communicate potential outcomes based on specific conditions.